Metal Building Roofs
A guide to metal building roof panels, pitches & styles
metal roof panels, pitches and styles
Index On This Page
1.Metal roof panels
2.Insulated metal roof panels
3.Skylight panels for metal buildings
4.Available roof pitches
5.Metal building roof styles

Metal Roof Panels
Through-Fastened Roofing (screw down)
A through-fastened roof panel is one where the roof panels are attached directly to the sub-structure with fasteners (treated screws) that penetrate through the panel sheets and into the roof purlins. After installation, the fastener locks the wall panel's overlapping sections into place and is visible on the panel's outside face. Through-fastened systems are also known as exposed fastener systems.
Through-fastening is typically used for buildings less than 60’ in width (measured in the direction of the roof slope). For larger buildings, stresses resulting from temperature expansion and contraction of exposed metal become more pronounced and more of a risk. As a result of the movement, through-fastened metal roofing panels can wear around the fasteners, leading to leaks.
Pros of Through-fastened roofing
- Most economical
- Ease and speed of installation
- Potentially vulnerable to leaking on large buildings
- Not as strong if in wind-prone areas, compared to standing seam panels
- Can be compromised if not installed correctly
PBR Panels: (Purling Bearing Rib)
PBR panels are special through-fastened roofing panels made of 26-gauge steel. All our suppliers include this panel as part of the standard building kit package (24-gauge is also available as an upgrade option).
PBR panels overlap where the panels meet, providing a larger joint, resulting in better leak protection against wind-driven rain or snow. The greater overlap also protects against snow or wind load and the weight of anyone walking on the roof.
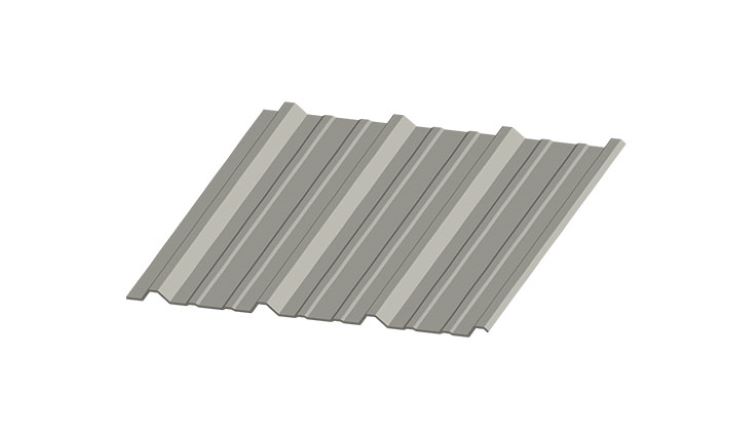

Through Fastener Metal Roofing Panel (PBR Panel)
Concealed-Fastened Roof Panels
There are no screws on the outside penetrating the panels, giving maximum weather-proofing. The overlap seam is above the roof deck, further enhancing the weather-proofing.
All the attachment is underneath the panel itself, attached to the purlins indirectly utilizing concealed steel clips with movable tabs. The clip bases are fastened to the purlins, while the roofing sheets are rolled around the tabs and can slide with the tabs relative to the clip bases – and the purlins. The result - the panels can expand and contract freely with temperature variation, giving both greater weather-proofing, rigidity, and longevity.
Pros of Standing Seam roofing
- Much better protection against leaks in all areas.
- Better protection against leaks in areas with temperature extremes.
- More visually attractive, with no visible screws.
- Stronger for areas prone to high winds.
- Longer lifespan before needing maintenance.
- No exposed screws that would catch dirt need tightening and potentially cause corrosion.
- A standing seam roof could last a lifetime with no maintenance.
- Greater cost. Twice as much or more compared to through-fastened roofs.
- More complex (and longer) installation process.
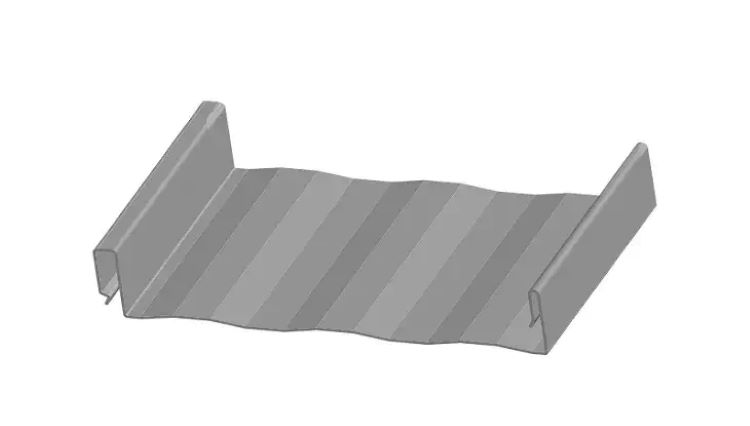
Insulated Metal Roof Panels
The panels consist of metal skins with a steel surface and an insulating foam core (usually either PIR or PUR foam)
Insulated panels are perfect for commercial, industrial, and institutional industries because they provide an unmatched weathertight seal and service life. They provide fast and simple installation and durable, dependable performance thanks to the most recent composite roof panel construction innovations.
Thermal properties, design flexibility, quick installation time, and great looks are why insulated roof panels are popular on modern commercial metal buildings.
Advantages:
- Superior insulation properties.
- Design flexibility.
- Fast installation times.
- Ideally suited to cold storage facilities due to high R-values.
- Relatively high cost.
- Special equipment is required for installation.
Colour Options for Metal Roofing
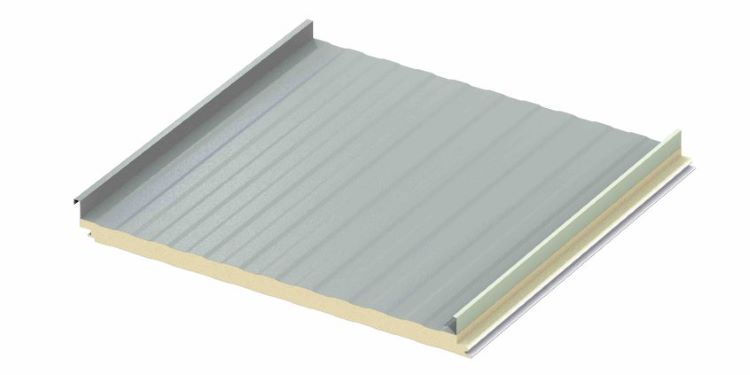
Insulated standing seam metal roof panel
Metal Roof Skylight Panels
This free light source could be a worthwhile investment, as you could greatly reduce your lighting costs. Natural lighting tends to increase employee satisfaction and reduce absenteeism. Skylights also enhance the value of your building for a possible future sale.
In metal building systems, skylights are typically produced by substituting translucent fiberglass or polycarbonate panels for the steel roofing panels. Fiberglass panels are the most cost-effective, but polycarbonate panels are often used when something stronger than fiberglass is required. Skylights for metal buildings are also available as insulated skylight panel units, with appropriate seals around the perimeter to prevent water intrusion.
Some manufacturers call these “roof-lights.” Translucent panels can also replace some wall panels to produce “wall-lights.” Skylights are typically positioned on either side of the roof's peak, which is why they are often sold in pairs. The optimal number of skylights will depend on the building size and use.
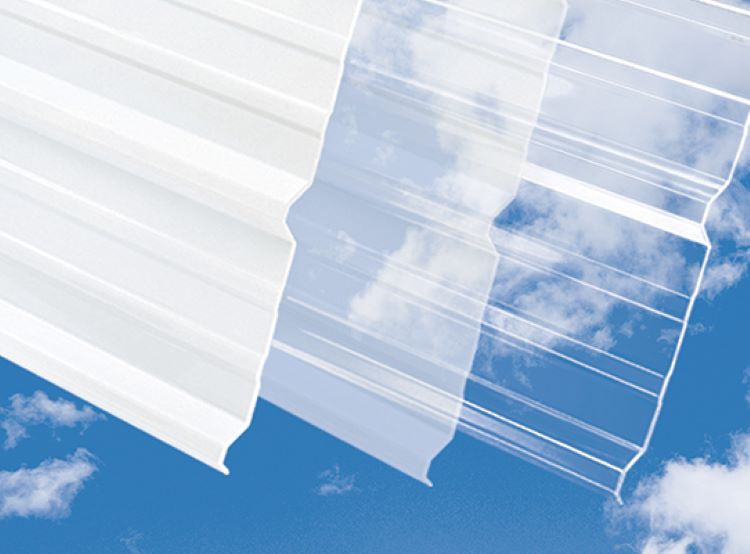
Modern polycarbonate skylight panels (as distinct from built skylight units) have several key benefits; they:
- Have dramatically greater impact resistance compared to traditional fiberglass panels (almost unbreakable).
- Are weather resistant to wind uplift and snow accumulation.
- Will protect the building against wind-driven rain or hail.
- Are made in a range of shapes to fit with most SM-RIB, PBR, and R metal panels.
- Can be clear, soft white, or a range of colors.
- Won’t yellow and will remain clear better than other glazing options.
- Have the best light transmission while protecting against UV.
- Can handle temperature extremes.

Metal Building Roof Pitch
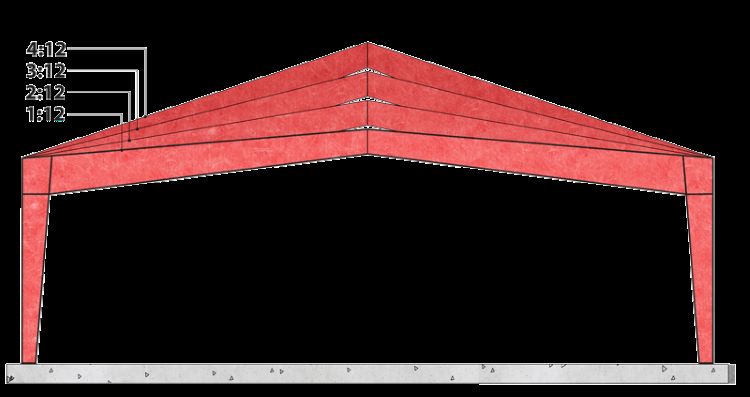
Roof Pitch (1:12 - 6:12)
Credit: ZHM Huawu Steel ©
Buildings with higher-pitch roofs utilizing colored metal roofing may provide better architectural appeal (particularly for residential applications).
Snow load is another consideration if your building will be in an area with significant snowfall. A steeper roof pitch will shed snow better.
Choosing a roof pitch
- Budget (a flatter roof is cheaper).
- The amount of clear space required down the middle of the building.
- On weather considerations such as snow load.
- And aesthetics - how the building fits in with surrounding structures.
Why choose a low-pitch roof?
- Easier to walk on and do maintenance.
- It is easier to mount AC units on the roof.
- Improved interior heating and cooling (no high roof cavity to heat/cool).
- Lower installation costs - less steel required for the roof structure.
Why choose a steep-pitch roof?
- Increased clear height in the middle of the building, allowing for taller racks and equipment.
- Better architectural appeal.
- Reduced snow loading on the roof structure.
Metal Building Roof Styles
Gable Roof
The gable roof design features two sloping sides that meet at the ridge (top). Many people refer to this as a pitched or peaked roof.
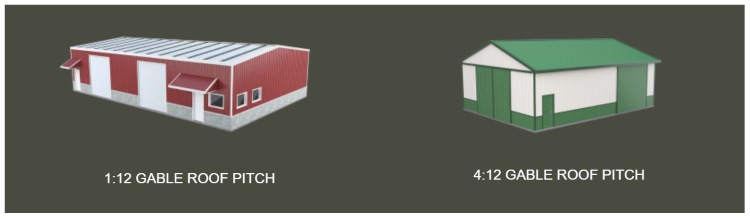
This roof style is practical, cost-effective, and attractive. You can achieve a very low pitch (1:12) or a very high pitch with this roof style (8:12). Most steep pitches are used to counteract heavy snow loads or achieve a certain aesthetic appeal. The adaptability of the gable roof allows it to be employed in any region or climate.
|
40x60 metal warehouse building 1:12 GABLE ROOF PITCH |
30x40 barn with sliding doors in the sidewall and end-wall 4:12 GABLE ROOF PITCH |
Among the key advantages of gable roofs are:
- Good water runoff.
- The style allows high interior clear height and makes loft space possible.
- Simple construction makes it the most economical option.
Available roof pitches: 1:12 to 6:12.
Hip Roof

Metal Hip Roof-Metal Carports Direct
Hip roofs are more difficult and a little more expensive to build than a simple gable roof. There is also less room in that upper building space. But the structure typically performs better in strong winds, so hip roofs are common in hurricane-prone areas.
A gable roof would likely be found on a utilitarian building - storage, warehouse, etc. A hip roof would be more commonly encountered in a public-use building, such as a library, community hall, office, or residence in a wind-prone area.
Key advantages of hip roofs include:
- They perform well in areas prone to high winds and rain.
- Allow for more appealing rooflines to be achieved than gable roofs.
Unlike other roof style options, hip roof designs require a minimum 3:12 roof pitch. Available roof pitches: 3:12 to 6:12.
Shed Roof (a.k.a. single-slope or single-pitch roof)
The single-slope roof is becoming increasingly popular, particularly among those who prefer a more contemporary look. The construction is simple, which results in one of the lowest-cost roof options.
Single-slope roofs are primarily used for low-rise, commercial applications, including strip malls, self-storage complexes, and offices. Typical uses include:
- Storage buildings and self-storage units.
- Single-story warehouses and industrial buildings.
- Office buildings.
- Retail buildings.
- Modern-style garages.
- Contemporary-style homes.
- Lean-tos.
Overhangs can be added to this roof style to increase its aesthetic appeal (see image below).
Available shed roof pitches: 1/2:12 to 6:12.

Single slope roof
Modern garage building with 1.5:12 pitch single-slope roofline
Credit: ZHM Huawu Steel

Single slope garage design with 3’ overhang
Credit: ZHM Huawu Steel
Gambrel Roof (Dutch-Barn Style)
It’s great for a two-story barn or barn-style home that needs additional storage or an office space above.
The roof's pitch also offers excellent drainage, making it especially suitable for areas with heavy rain or snow.
Typical pitches:
Upper roof: 2:12 - 3:12
Lower roof: 5:12 - 6:12
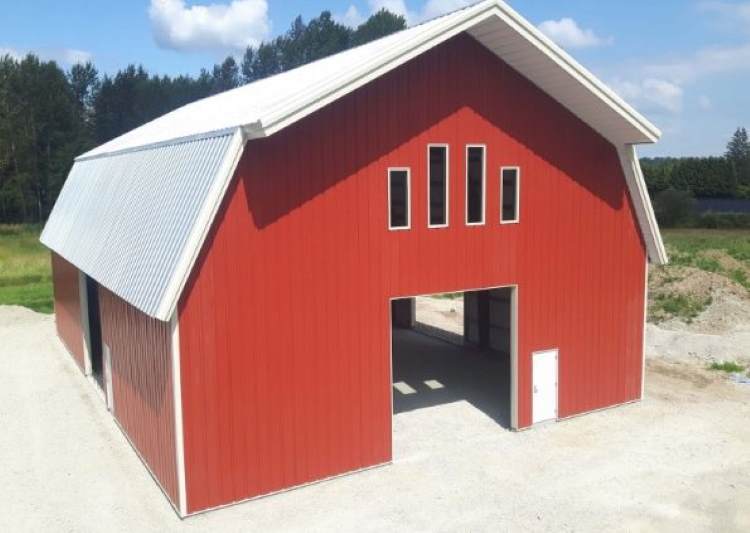

Gambrel Roof
Monitor Roof (American Barn Style)
Originally used in horse barns and industrial buildings, these roofs are gaining popularity in barn-style homes (“barndominiums”) because of their additional height and light. The raised center roof can also serve as a storage loft. Farmers can store cattle feed in the center area and could add chutes to make it easier to feed the animals below.
A monitor roofline is also useful for storing overheight vehicles, such as RVs and motor homes, in the middle, with lower doors on either side.
The monitor height and pitch can be engineered to suit your specific requirements.
Roof pitches can be the same for both roof portions or be different to create your own unique look.
Typical pitches:
Upper roof: 4:12 - 6:12
Lower roof: 3:12 - 5:12

Credit: ZHM Huawu Steel
Quonset Buildings
A Quonset hut Building could be a great choice for those seeking simplicity and a low price point. For generations, Quonset huts have been meeting the needs of the military, industry, and backyard hobbyists seeking safe, dependable, and economical storage space. They are so easy to erect that 75% of Quonset buyers choose to DIY build.
Quonset buildings (a.k.a. arch buildings) can be great for business, industry, modern farms, and families. They are suitable for barns, food or machinery storage, hangars, stables, and even homes.
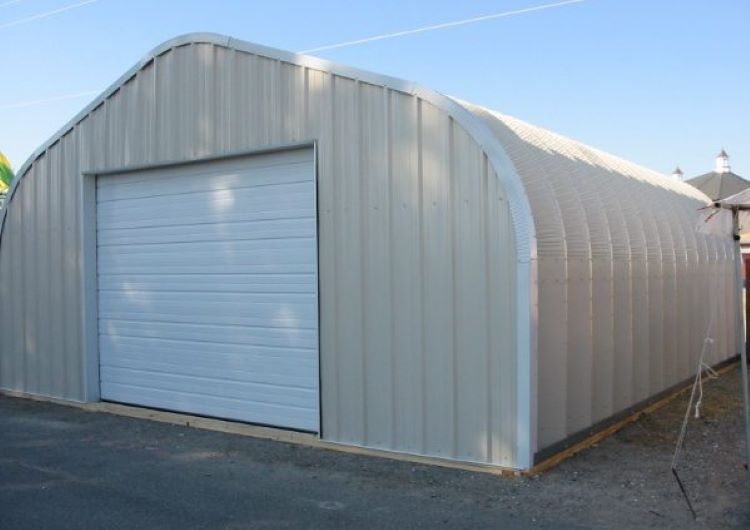

Quonset-style building
Common Questions
How do you calculate pitch on a steel building roof?
To calculate the pitch on a steel building roof, you will need to know the rise and the run of the roof. The rise is the vertical measurement from the top of the roof to the point where the roof meets the wall. The run is the horizontal measurement from the top of the roof to the center of the building.
To calculate the pitch, divide the rise by the run and then convert the answer to a ratio. For example, if the rise is 4 feet and the run is 12 feet, the pitch would be 1/3 or a "4 in 12" pitch.
What is the roof trim called on a metal building?
The roof trim on a metal building is typically called a "ridge cap" or "ridge cap trim." It is a trim piece that is used to cover the seam where two roof panels meet at the peak or ridge of the roof. It is designed to protect the seam from water infiltration and to give the roof a finished, professional look. Ridge cap trim is typically made of the same material as the roof panels, such as Galvalume, Galvanized steel or aluminum.
How do you reduce noise of metal roof on metal building?
There are several ways to reduce the noise of a metal roof on a metal building. Some include:
Insulation: Installing insulation can help to absorb sound and reduce noise.
Acoustic barriers: Installing an acoustic barrier, such as foil-faced insulation or a mass-loaded vinyl barrier, can also help to reduce noise.
Roof underlayment: Utilizing a special type of roof underlayment such as a synthetic underlayment that is specifically designed to reduce noise
Sound-deadening paint: Applying a sound-deadening paint or coating to the metal roof can also help to reduce noise.
It's important to note that some of these solutions may not be suitable for all types of metal roofs, so it's best to consult with a professional before proceeding.
Would you like to see more information and images of ZHM’s Metal Steel Structure Building Metal Building Roofs ? Visit our Photo Gallery.
HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
ZHM’s world-class team — together with our raw material suppliers and subcontractors — works to solve your most challenging design, engineering, farbrication or construction issues.
Contact ZHM by telephone at +86 135-8815-1981 (wechat and whatsapp) or send us your questions via email to info@zhmsteelworks.com
- Pre:None
- Next:Design Criteria of Reefer Rack 2024/6/4

