Steel Structure Design Principles A Comprehensive Guide
Home » Steel Building » Steel Structure Design Principles: A Comprehensive Guide
Comprehensive structural analysis and calculations are required during the design process to ensure the structure can withstand the necessary loads and external forces, such as seismic forces. Relevant steel structure design codes and standards also need to be followed. Steel structure design requires advanced design tools and technologies, such as computer-aided design software and three-dimensional modeling technology, to improve design efficiency and accuracy.
Table of Contents
1.1.Load for Steel Structure Design
1.1.1.Loads mainly include the following types:
1.1.2.Calculation formula of seismic force: seismic force = self-weight × seismic coefficient
1.2.Structural stability for steel structure design
1.2.1.Cross-sectional shape
1.2.2.Material strength
1.2.3.Cross-sectional dimensions
1.2.4.Member length
1.3.Design principles for structural stability:
1.3.1.The stability of the overall building structure needs to be considered
1.3.2.The calculation drawings must be consistent with the actual calculations.
1.3.3.The stability calculation of the steel structure must be consistent with the internal details.
1.4.Aesthetic for Steel Structure Design
1.5.In conclusion
Steel Structure Design
Load for Steel Structure Design
steel structure load
Loads mainly include the following types:
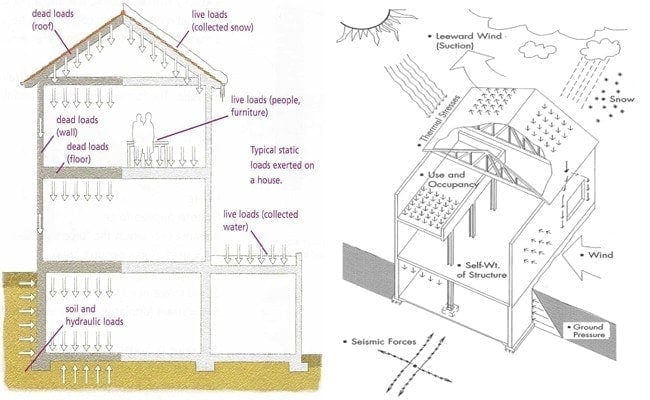
Live load: Live load, or variable load, is the use or occupation load and naturally occurring natural load imposed on the structure caused by people, materials, and vehicles, such as steel structure building floor live load, roof live load, roof area ash load, vehicle load, crane load, etc.
Wind load: Wind load, also known as wind dynamic pressure, is the pressure produced by air flow on engineering structures. Wind load is related to essential wind pressure, topography, ground roughness, height from the ground, and building shape.
Snow load: Snow load refers to the snow pressure acting on the top surface of a building or structure for calculation. Snow load is formed by snow accumulation and is a spontaneous meteorological load. The size of the snow load value mainly depends on the amount of snowfall in each region based on meteorological data, the roof form, the geometric size of the building, and the regular use of the building.
Seismic load: Seismic load is also called seismic force. A general term for the inertial force, earth pressure, and water pressure a structure experiences due to an earthquake. Since horizontal vibration has the most significant impact on buildings, only horizontal vibration is generally considered.
Calculation formula of seismic force: seismic force = self-weight × seismic coefficient
In terms of building weight, steel structures are lighter in weight than concrete structures. The self-weight of steel structures is generally about two-thirds or one-half of that of steel-concrete systems. According to the above calculation rules, a lightweight steel structure building will significantly reduce and mitigate seismic forces, thereby protecting the stability of the entire building.
The purpose of load analysis is to ensure that the building can operate safely under various external force factors and that no structural damage or collapse will occur, even in extreme situations. It can also help designers choose appropriate steel materials for design.

steel structure design
Structural stability for steel structure design
A steel structure’s stability coefficient (also called buckling coefficient) refers to the ratio of the maximum load a component can withstand when subjected to external forces relative to the ultimate load. Generally speaking, the higher the stability coefficient, the better the stability of the element. Here are some critical structural stability considerations:
Cross-sectional shape
Material strength
Cross-sectional dimensions
Member length
Design principles for structural stability:
In architectural design, we usually first consider the plane layout of the building, such as the frame design on the architectural drawings. But to ensure the facility will not collapse, we must reasonably arrange the support system in the steel structure design. This means that the plane design of the building must be consistent with the three-dimensional structure of the building, taking into account not only the plane’s stability but also the building’s foundation stability.
The calculation drawings must be consistent with the actual calculations.
In the design of multi-story or high-rise buildings, data calculations are usually performed using frame structures rather than starting from the stability of the steel structure. In actual calculations, we need to use the coefficients of the virtual frame columns to ensure the overall strength of the steel structure. To meet the stability of steel structure design, we need to set specific calculation templates, which can be used in subsequent calculations to obtain reliable data.
The stability calculation of the steel structure must be consistent with the internal details.
We must ensure consistent structural design and calculation results when performing specific data calculations. In addition to the main frame structure calculations, we also need to pay attention to the details of the steel structure, such as the bending capacity of the connection points and the eccentricity of the rods. These details are equally important.

steel structure design
Aesthetic for Steel Structure Design
The appearance of a building is the first impression given to people. Beautiful shape and appropriate proportions all affect the building’s appeal to people. Of course, choosing different materials will also significantly impact the overall structure.
The light and view of the building are also a significant factor that tests designers. Reasonable architecture should be integrated with the natural environment, have perfect light and vision, and can bring people a more pleasant living experience.
Cultural and historical background. Different countries have different cultures and histories and other architectural styles. The designer must conform to the local architectural style to integrate the building into the local community.
In conclusion
- Pre:None
- Next:How to Design and Fabricate St 2024/4/26
